Evaluation: Perceived Feeling of Control
Method
- To learn more about the difference between qualitative and quantitative evaluation look at this card.
- To quantitatively evaluate the perceived feeling of control, we created our own three-item scale, partially inspired by the autonomous vehicle acceptance model (AVAM) questionnaire [1].
- Around 30-40 testers are recommended for quantitative research.
- The three items are rated via a 7-point
Likert scale (strongly disagree – strongly agree):
- I would have adequate control over the information given by the vehicle.
- I would have adequate control to get the information that I need about the ride.
- I have the feeling of being in control during the ride
Data Analysis
Score Calculation
To get the score for the perceived feeling of control (x) for each participant, you have to sum up the three items and divide them by 3.
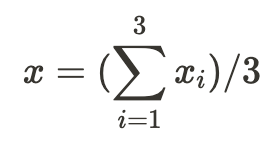
To get the final score for the perceived feeling of control (c) for all participants, you have to sum up all the perceived feeling of control scores (x) and divide them by the number of participants (n).
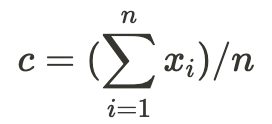
Calculate the Cronbach Alpha value for your data. The Cronbach Alpha values should be greater than 0.7. It resembles the internal consistency of your scale. Low values could indicate that some items were interpreted unexpectedly by participants. If your Cronbach Alpha Score is low, you should be careful when interpreting the results. A free online calculator can be found here. Insert all your raw values, one column per item. Do not calculate the Alpha Score for each question, but for all 3 safety questions at once.
Comparing two or more groups statistically
Reporting Results Sample
“Providing feedback significantly increased the perceived feeling of control compared to not providing feedback (Mfeedback = 3.74, Mno-feedback = 1.65, p < .05)"
Interpreting the Results
- The higher the score, the better the perceived feeling of control.
- It is recommended to perform A/B testing to better understand the values and see how much they differ. For example, one group is provided with transparency-communication, and the other group is not.
- Furthermore, suppose qualitative data is present (e.g. interviews or think-aloud, see section Qualitative Evaluation). In that case, you should use it for interpreting and discussing the quantitative results of the perceived feeling of safety to get a better understanding.
Sources
[1] - Hewitt, Charlie, et al. "Assessing public perception of self-driving cars: The autonomous vehicle acceptance model." Proceedings of the 24th international conference on intelligent user interfaces. 2019.